对目标检测模型 PR 曲线的原理分析和实现
PR曲线其实就是以准确率(Precise)为横轴,召回率(Recall)为纵轴的曲线,定义很简单,但是我们立即会产生一个疑问,那就是对于一个确定的模型,怎么准确率咋还能变化呢?所以要理解 PR 曲线,首先需要知道准确率和召回率是怎么变化的。
我们知道,准确率指的是准确检测的物体占总检测物体的比例(需要注意的是,我们的分析都是建立在单一类别之上的),比如一次测试过程,我们检测到了 M 个物体,但实际上只有 P 个物体是被准确检测到的,其他都属于误检,那么准确率就是 P / M。而召回率则是准确检测的物体占总的物体的比例,还是同样的测试,假如这批样本中共有 N 个物体,那么召回率就等于 P / N。准确率的分母是检测到的物体总数量,召回率的分母是实际物体总数量,所以准确率又叫查准率,召回率又叫查全率。
一般目标检测模型的输出会附带一个自信度(confidence),介于 0 到 1 之间,自信度越大表示其检测准确的概率越大,那么,我们就需要抉择了,如果一个检测实例的自信度等于 0.6,是否认为其检测准确?0.5 呢? 0.4 呢?显然,这是一个不好回答的问题,0.8 太严格,0.2 太宽松,都不好。于是,我们只有劳烦一下,在每个自信度上分析一次。显然在每个自信度级别上计算的准确率和召回率是不一样的,这就是为什么会有一根曲线的原因了。
PR曲线的原理就是这样,接下来我们考虑具体的实现问题。首先,我们需要一张表来记录检测结果,其 header 如下
|gt_id|pred_id|iou|confidence| |–|–|–|–|–|–|
依次为 Ground Truth id、预测id、交并比以及自信度,对于一张图片来说,其物体实例有 N 个,检测结果有 M 个,为了将 pred 和 gt 对应起来,我们需要计算它们的 IOU 矩阵,这是一个 M by N 的矩阵,其第 i 行第 j 列的值是第 i 个pred 与第 j 个 gt 的交并比,然后我们需要找到每列的最大值,也就是每个 pred 匹配上的 gt,但是这里存在一个问题,有可能同一个 gt 被多个 pred 匹配上了,这时就需要对 IOU 排序,以最大的 IOU 作为正样本。以 detectron2 提供的工具函数 pairwise_iou 为例,代码如下
pred_boxes: Boxes = ...
gt_boxes: Boxes = ...
iou_matrix: torch.Tensor = pairewise_iou(pred_boxes, gt_boxes)
ious, gt_ids = iou_matrix.max(dim=1)
这里 iou_matrix 的每一行就是当前 pred_box 与所有 gt_box 的交并比。通过 iou_matrix.max(dim=1) 方法找到每一行的最大值组成向量 ious,而最大值的列索引组成向量 gt_ids,也就是每个 pred_box 对应的 gt_box id。为了构建上表,还需要生成 pred_id 以及 confidence,其中 pred_id 可以按预测实例的顺序生成,为了区分图片,可以在前缀上加上图片id,confidence 就是算法输出的得分值。
df_i = pd.DataFrame({
"gt_id": [f"{image_id}_{i}" for i in gt_ids.cpu().numpy().tolist()],
"predict_id": [f"{image_id}_{i}" for i in range(len(gt_ids))],
"iou": ious.cpu().numpy().tolist(),
"confidence": output["instances"].scores.cpu().numpy().tolist()
}
不难发现,在上述过程中,对于每个 pred_box,仅有一个 gt_box 与之对应,但是有可能会出现多个 pred_box 对应同一个 gt_box 的情况,这个问题我们在构建出完整的表之后解决。
这是一张图片的情况,对于多张图片,还需要拼接连续
df=pd.concat((df, df_i), axis=0)
在得到类似于下面这张表之后,接下来开始划分正预测,即 True Positive。
| index | gt_id | predict_id | iou | confidence |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0006990_1 | 0006990_0 | 0.922708 | 0.999956 |
| 1 | 0006990_5 | 0006990_1 | 0.880718 | 0.999952 |
| 2 | 0006990_14 | 0006990_2 | 0.986290 | 0.999944 |
| 3 | 0006990_26 | 0006990_3 | 0.942946 | 0.999930 |
| 4 | 0006990_24 | 0006990_4 | 0.926946 | 0.999927 |
首先,需要确定一个 IOU 阈值,当 gt 与 pred 的 iou 大于该值的时候,则认为此预测为 TP,比如,将其设为 0.5
df["TP"] = df["iou"] > 0.5
然后,我们来解决同一个 gt 匹配多个 pred 的问题,解决方法是将最大 IOU 的 pred 设为 TP,从编程的角度来看,我们首先按 gt_id 分组,然后找到每组的最大 IOU,这时对应的 predict_id 就是最佳匹配,将它们设为 TP
max_iou=df[["gt_id", "iou"]].groupby("gt_id").max()
best_match_df=df[["gt_id", "iou", "predict_id"]].merge(max_iou, how="inner", on = ["gt_id", "iou"])
best_match_df=best_match_df.drop(columns=["iou"])
best_match_df["best_match"]=pd.Series([True for _ in range(len(best_match_df))])
得到下表
| index | gt_id | predict_id | best_match |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0006990_1 | 0006990_0 | True |
| 1 | 0006990_5 | 0006990_1 | True |
| 2 | 0006990_14 | 0006990_2 | True |
| 3 | 0006990_26 | 0006990_3 | True |
| 4 | 0006990_24 | 0006990_4 | True |
然后再以 gt_id 和 predict_id 为key,merge 回 df 表,这里采用 outer merge,让非最佳匹配对的 best_match 为 False
df = df.merge(best_match_df, how="outer", on=["gt_id", "predict_id"]).fillna(False)
此时某些行的 TP 列和 best_match 列可能不同,也就是说,某些 pred 的 IOU 虽然大于阈值,但是还有比它更好的匹配框,所以应该将其 TP 设为 False,表现为 TP 列 best_match 列的逻辑与关系运算
df["TP"] = df["TP"] & df["best_match"]
这样我们就完成了对预测数据的处理,接下来开始计算每个 confidence 下的 Precise 和 Recall。首先按 confidence 从大到小排序,并生成每个 confidence 作为阈值的情况下的 TP 数量和 pred 数量,也就是前面提到的 P 和 M, 而 gt 数量 N 是常数。
df = df.sort_values(by="confidence", ascending=False)
M = pd.Series([i + 1 for i in range(len(df))])
P = pd.Series([tp[0:i+1].sum() for i in range(len(df))])
precise = P / M
recall = P / N
接下来,我们以文本检测网络 DBNet 的官方预训练模型 (td500_resnet50) 为例,来看看对 MSRA-TD500 数据集的 PR 曲线。首先定义一些辅助函数
import os
os.environ['KMP_DUPLICATE_LIB_OK'] = 'True'
from concern.config import Configurable,Config
import numpy as np
import math
import torch
from torchvision.io import read_image
from torchvision.io import ImageReadMode
import torch.nn.functional as F
import glob
import math
import cv2
from shapely.geometry import Polygon
import pandas as pd
def load_eval_model():
"""
加载模型
"""
args={
"resume": "./checkpoints/td500_resnet50",
"box_thresh": 0.4,
# "thresh": 0.8,
"log_dir": "./logs",
"visualize": True,
"image_short_side": 736,
"polygon": False,
"result_dir": "./result_dir"}
config = Config()
experiment_args=config.compile(config.load("./experiments/seg_detector/td500_resnet50_deform_thre.yaml"))['Experiment']
experiment_args.update(cmd=args)
experiment = Configurable.construct_class_from_config(experiment_args)
experiment.load("evaluation", **experiment_args)
structure = experiment.structure
model_path = args["resume"]
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
model = structure.builder.build(device)
state_dict = torch.load(model_path, map_location=device)
model.load_state_dict(state_dict)
model.eval()
return model, structure
def load_image(path, short_side=736):
"""
加载图片
"""
RGB_MEAN = torch.Tensor([122.67891434, 116.66876762, 104.00698793]).view(-1, 1, 1)
img = read_image(path, ImageReadMode.RGB)
c, h, w = img.shape
original_size = (h, w)
if h < w:
new_height = short_side
new_width = int(math.ceil(new_height / h * w / 32) * 32)
else:
new_width = short_side
new_height = int(math.ceil(new_width / w * h / 32) * 32)
img = img.unsqueeze(0).float()
img = F.interpolate(img, size=(new_height, new_width), mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
img = img - RGB_MEAN
img /= 255.0
return img, original_size
def read_ground_truth(path):
"""
读取 ground truth 数据
:param path: ground truth 文件路径
"""
with open(path, 'r') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
lines = [line.strip() for line in lines]
gt_boxes = []
for line in lines:
index, diffcult, x, y, w, h, theta = line.split(' ')
x, y, w, h, theta = float(x), float(y), float(w), float(h), float(theta)
cx = x + w / 2
cy = y + h / 2
x1 = cx - w / 2 * math.cos(theta) - h / 2 * math.sin(theta)
y1 = cy - w / 2 * math.sin(theta) + h / 2 * math.cos(theta)
x2 = cx + w / 2 * math.cos(theta) - h / 2 * math.sin(theta)
y2 = cy + w / 2 * math.sin(theta) + h / 2 * math.cos(theta)
x3 = cx + w / 2 * math.cos(theta) + h / 2 * math.sin(theta)
y3 = cy + w / 2 * math.sin(theta) - h / 2 * math.cos(theta)
x4 = cx - w / 2 * math.cos(theta) + h / 2 * math.sin(theta)
y4 = cy - w / 2 * math.sin(theta) - h / 2 * math.cos(theta)
x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3, x4, y4 = int(x1), int(y1), int(x2), int(y2), int(x3), int(y3), int(x4), int(y4)
gt_boxes.append([[x1, y1], [x2, y2], [x3, y3], [x4, y4]])
return gt_boxes # n x 4 x 2
def pairwise_iou(gt_boxes, pred_boxes):
"""
计算 gt 列表与 pred 列表之间的 IOU 矩阵
:params gt_boxes: gt 列表 [n, 4, 2]
:params pred_boxes: pred 列表 [m, 4, 2]
"""
iou_matrix = np.zeros((len(pred_boxes), len(gt_boxes)))
for i in range(len(pred_boxes)):
for j in range(len(gt_boxes)):
gt_polygon = Polygon(gt_boxes[j])
polygon = Polygon(pred_boxes[i])
iou_matrix[i, j] = polygon.intersection(gt_polygon).area / polygon.union(gt_polygon).area
return iou_matrix # m x n
然后开始对测试集作预测,并将结果写入数据框
test_dir = "./MSRA-TD500/test"
img_paths = glob.glob(test_dir + "/*.jpg")
df = pd.DataFrame()
N = 0 # 所有图片上的文本实例数量
for img_path in img_paths:
filename=os.path.basename(img_path)
gt_path=test_dir + "/" + os.path.splitext(filename)[0] + ".gt"
gt_boxes = read_ground_truth(gt_path)
img, original_size=load_image(img_path)
batch = {
"filename": [img_path],
"shape": [original_size],
"image": img
}
with torch.no_grad():
pred = model.forward(batch, training = False)
output = structure.representer.represent(batch, pred, is_output_polygon=False)
a, b = output
pred_boxes = a[0]
confidence = b[0]
pred_boxes=pred_boxes.tolist()
N += len(gt_boxes)
if len(pred_boxes) == 0 or len(gt_boxes) == 0:
continue
iou_matrix=pairwise_iou(gt_boxes, pred_boxes)
gt_ids = iou_matrix.argmax(axis=1)
ious=iou_matrix[range(len(iou_matrix)), gt_ids]
df_i = pd.DataFrame(
{
"gt_id": [f"{filename}_{i}" for i in gt_ids],
"pred_id": [f"{filename}_{i}" for i in range(len(pred_boxes))],
"iou": ious,
"confidence": confidence
}
)
df = pd.concat([df, df_i], axis=0)
最后,计算 PR 曲线
df["TP"] = df["iou"] > 0.5 # 以 0.5 为 IOU 阈值设置 True Positive
## 解决多个 gt 对应同一个 pred 的问题
max_iou=df[["gt_id", "iou"]].groupby("gt_id").max()
best_match_df=df[["gt_id", "iou", "pred_id"]].merge(max_iou, how="inner", on = ["gt_id", "iou"])
best_match_df=best_match_df.drop(columns=["iou"])
best_match_df["best_match"]=pd.Series([True for _ in range(len(best_match_df))])
df = df.merge(best_match_df, how="outer", on=["gt_id", "pred_id"]).fillna(False)
## 解决 IOU 大于阈值但不是最佳匹配的对
df["TP"] = df["TP"] & df["best_match"]
## 对 confidence 按从大到小排序
df = df.sort_values(by="confidence", ascending=False)
## 大于各个 confidence 的预测数量
M = pd.Series([i + 1 for i in range(len(df))])
## 大于各个 confidence 的正预测数量
tp = df["TP"]
P = pd.Series([tp[0:i+1].sum() for i in range(len(df))])
precision = P / M
recall = P / N
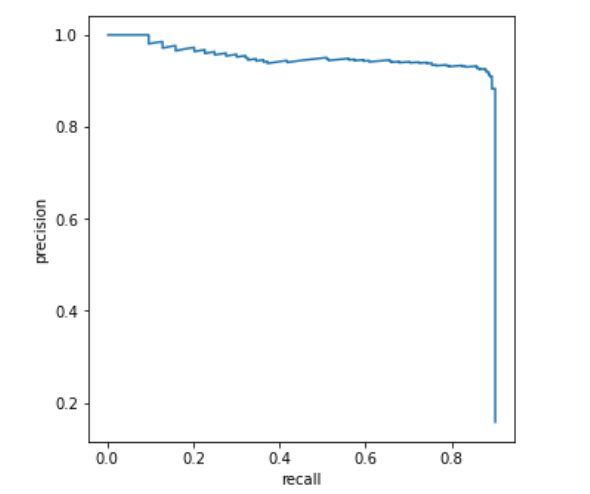
可以看到 PR 曲线的特点是,准确率越高,召回率就越低,这是显而易见的,当 confidence 阈值设置得很大的时候,大部分正预测都将是准确的,而因为门槛太高,导致很少有 pred 达到要求,所以占总的 gt 数量极少,于是召回率就低, 反之亦然。
如果查看 precision 和 recall 两个数组,可以发现当 p = 0.916 时,r = 0.72,这一结果与原论文(r = 0.79)的有一定的差距,但考虑到参数设置的差异,这种波动应该是在合理的范围内。